Understanding Measles
Measles is a highly contagious viral infection that primarily affects children. It is spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. While measles can be prevented with vaccination, it remains a significant public health concern in many parts of the world.
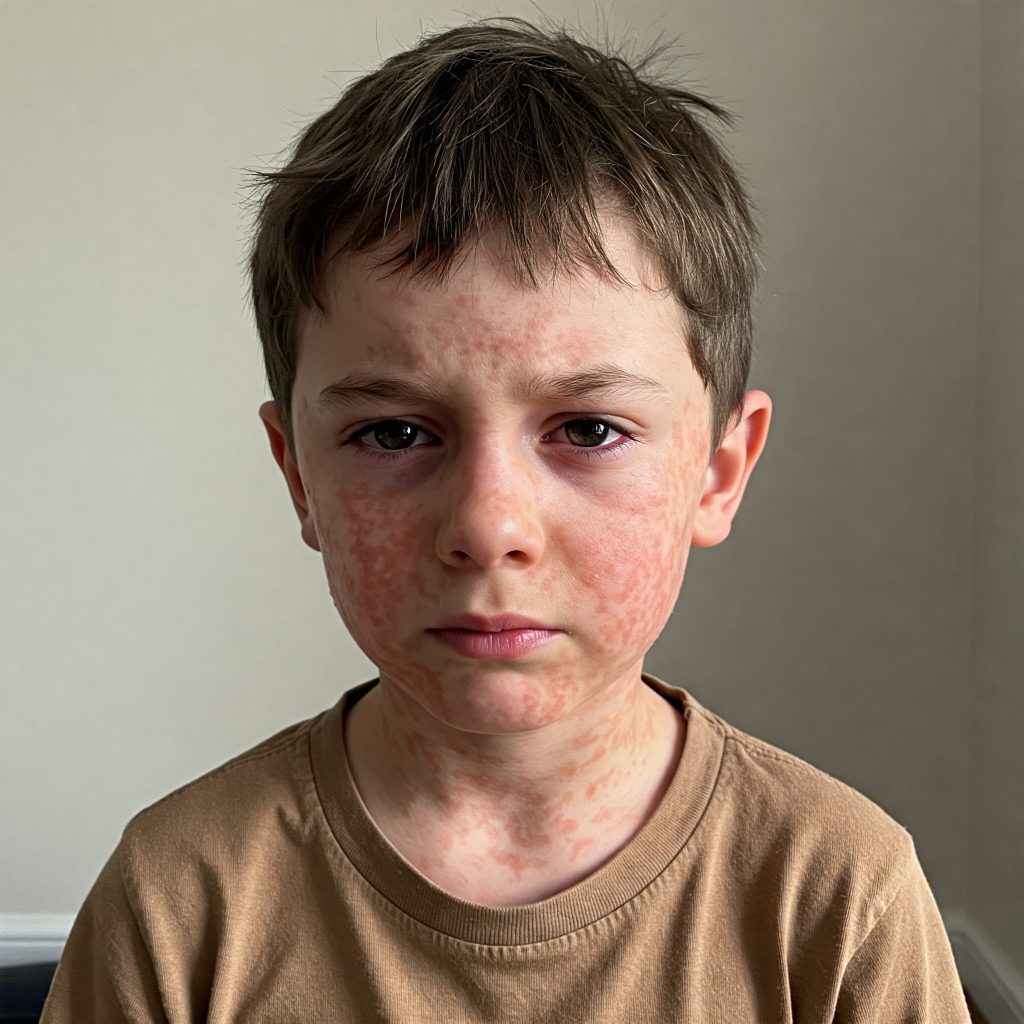
Symptoms of Measles
The symptoms of measles typically appear 7-14 days after exposure to the virus. They include:
- High fever
- Cough
- Runny nose
- Watery eyes
- Sore throat
- Tiny white spots inside the mouth (Koplik’s spots)
- Red, blotchy rash that spreads across the body
Complications of Measles
While most children recover from measles without complications, some may experience more serious health problems, such as:
- Ear infection
- Diarrhea
- Pneumonia
- Encephalitis (inflammation of the brain)
Prevention of Measles
The most effective way to prevent measles is through vaccination. The measles vaccine is safe and highly effective, and it is 1 routinely administered to children in two doses.
Other preventive measures include:
- Avoiding contact with people who have measles
- Practicing good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently
- Staying home if you are sick
If you think you or your child may have measles, it is important to see a doctor right away. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent serious complications.
Leave a Reply