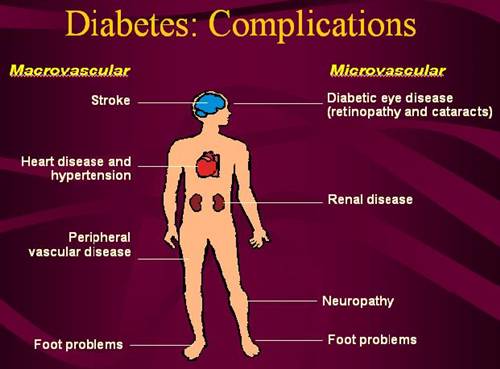
When the body has problem to control blood glucose in a normal condition (3-8 mmol/liter) and delivering it to the rest of the body for energy, it means that the patient is suffering diabetes mellitus. This is because of the lack or inability to use insulin which is required to transport glucose from blood to the body cells.
The best way to control diabetes is by the lifestyle changes which combined the healthy diet and exercise. Actually obese or overweight patient have insensitive insulin receptor because of excessive body fat.
Physical activity helps your muscle cells use blood glucose (cells need glucose for energy). Exercise thus makes those cells more sensitive to insulin. Here’s how.
When you exercise, both your heart rate and breathing increased. These provide more oxygen to your muscle. Our body ideally needs plenty of oxygen to help it burn fuel to make energy. The fuel the muscles need comes from:
– glucose stores in the muscle (glycogen)
– fat stores
– glucose made by liver
To put in another way, as your muscle contract during exercise, they use sugar for energy. To meet this energy need, sugar is removed from your blood during and after exercise, which lowers your blood sugar level. In other words, exercise allows your body to available insulin more efficiently to bring sugar into your cells, and ultimately lower your blood sugar.
Aerobic exercise increases insulin sensitivity and along with proper nutrition, helps restore normal glucose metabolism by decreasing body fat. Strength training (also known as resistance or weight training) also decrease body fat by raising the metabolism. Its main benefit, however, is increasing glucose uptake by the muscles and enhancing the ability to store glucose.
Aerobic exercise:
Since many type 2 diabetics are sedentary and overweight, low impact exercise such as brisk walking or stationary cycling is recommended. Their goal should be to exercise 5 times per week, up to 40-60 minutes per session at a moderate intensity. This level of exercise can be reached gradually, starting as low as 10-20 minutes a few times a week for a person who has never exercised.
Strength training:
It can increase lean mass, which will help in weight management as well as increase glucose uptake by the muscles and help the body to store glucose. Strength training program are designed around a person’s needs, desires, level of conditioning and time factors.
Their goal should be to exercise 5 times per week, up to 40-60 minutes per session at a moderate intensity. This level of exercise can be reached gradually, starting as low as 10-20 minutes a few times a week for a person who has never exercised.
In a nutshell, everyone, especially diabetic patient should monitor their blood sugar level during physical activity. This is because the exercises may decrease or increase the blood sugar level. You are advised to consult your doctor before undergoing any exercise program.

Leave a Reply