For decades, we’ve been told that our genes are our destiny. We inherit traits from our parents, and that’s largely considered unchangeable. However, a groundbreaking field of science is challenging this notion: epigenetics. This discipline explores how environmental factors, including diet, can influence gene expression without altering the underlying DNA sequence. Nutritional epigenetics, in particular, is revealing the profound impact of food on our genetic blueprint.
Imagine your genes as a set of blueprints for a house. Epigenetics is like adding or removing layers of paint to those blueprints, affecting which parts are visible and accessible to builders. Nutrition plays a pivotal role in this process, acting as the painter that can either enhance or obscure the blueprint’s potential.
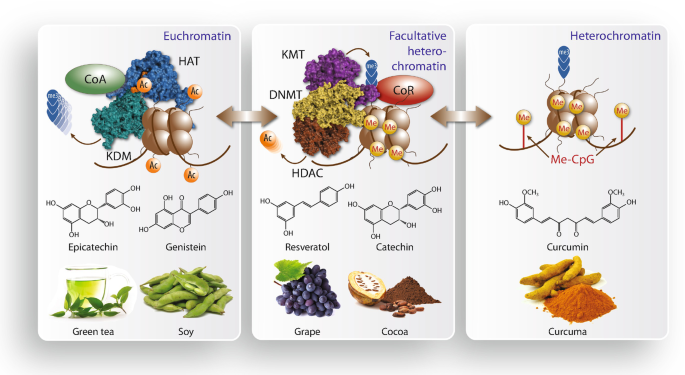
By understanding nutritional epigenetics, we unlock the power to harness food as a tool for optimizing health and well-being. It’s a paradigm shift that moves beyond simply counting calories and macronutrients to a deeper understanding of how our dietary choices shape our genetic expression.
Understanding Epigenetics
Before diving into the world of nutrition, it’s essential to grasp the basics of epigenetics. While our DNA remains constant, the way it’s packaged and read can be influenced by various factors, including diet, stress, and environmental toxins.
Two primary epigenetic mechanisms are at play:
- DNA methylation: This involves adding a chemical tag called a methyl group to DNA, which can turn genes “off.”
- Histone modification: Proteins called histones package DNA. Modifications to these histones can affect how accessible the DNA is for gene expression.
These epigenetic changes can be passed down through generations, highlighting the importance of dietary choices for both individuals and future offspring.
The Role of Nutrition in Epigenetics
Our diet provides the building blocks for life, supplying the nutrients necessary for growth, repair, and energy production. But beyond these fundamental roles, food also acts as a potent modulator of gene expression.
Certain nutrients, often referred to as “epigenetic nutrients,” are particularly influential:
- Folate and B vitamins: These are essential for DNA methylation and play a crucial role in preventing birth defects and chronic diseases.
- Phytochemicals: Found in plants, these compounds exhibit powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, influencing gene expression related to disease risk.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: These healthy fats are involved in gene regulation and have been linked to reduced inflammation and improved brain health.
By consuming a diet rich in these nutrients, we can create an epigenetic environment that supports optimal health.
Nutritional Epigenetics and Disease
The implications of nutritional epigenetics for disease prevention and management are profound. Chronic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer have been linked to epigenetic alterations. By making dietary changes, individuals may be able to influence their susceptibility to these diseases.
For example, studies have shown that diets high in processed foods and red meat can lead to epigenetic changes associated with increased cancer risk. Conversely, plant-based diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are linked to a lower risk of chronic diseases.
Practical Applications of Nutritional Epigenetics
While the science of nutritional epigenetics is still in its early stages, there are practical steps individuals can take to harness its power:
- Prioritize whole foods: Opt for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Minimize processed foods: These often contain additives and unhealthy fats that can contribute to negative epigenetic changes.
- Consider personalized nutrition: While research is ongoing, there’s potential for tailoring diets based on individual genetic and epigenetic profiles.
- Support a healthy gut microbiome: The gut microbiome plays a role in epigenetic regulation. Consume fermented foods and fiber-rich foods to nourish beneficial gut bacteria.
Conclusion
Nutritional epigenetics is a game-changer in our understanding of health and well-being. It empowers us to take control of our genetic destiny through dietary choices. By unlocking the power of food, we can create an epigenetic environment that supports optimal health and longevity.
It’s important to note that while the potential of nutritional epigenetics is exciting, more research is needed to fully understand its complexities. However, the evidence is clear: our diet plays a far more significant role in our health than we ever imagined.
Leave a Reply