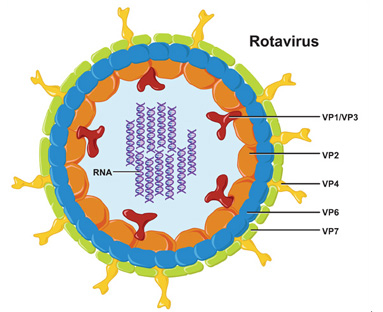
Rotavirus is the most common cause of severe diarrhea among infants and children throughout the world. There are different strains of rotavirus and multiple infections by different strains may occur.
Rotavirus symptoms
A rotavirus infection usually starts within two days of exposure to the virus. Initial symptoms are a fever and vomiting, followed by three to seven days of watery diarrhea. The infection can cause abdominal pain as well.
In adults, a rotavirus infection may cause only mild signs and symptoms or none at all.
Rotavirus infection is highly contagious and the incubation period is typically about two days.
Rotavirus causes
Rotavirus is present in an infected person’s stool several days before symptoms appear and for up to 10 days after symptoms subside. The virus spreads easily through hand to mouth contact throughout this time. If you have rotavirus and you don’t wash your hands after using the toilet — or your child has rotavirus and you don’t wash your hands after changing your child’s diaper or helping your child use the toilet — the virus can spread to anything you touch, including food, toys and utensils. If another person touches your unwashed hands or a contaminated object and then touches his or her mouth, an infection may follow. The virus can remain infectious on surfaces for weeks or longer if the area isn’t disinfected.
Because there are many types of rotavirus, it’s possible to be infected more than once, even if you’ve been vaccinated. However, repeat infections are typically less severe.
Rotavirus spreads easily. Good hygiene like handwashing and cleanliness are important, but are not enough to control the spread of the disease.
Rotavirus vaccine is the best way to protect your child against rotavirus illness. Most children (about 9 out of 10) who get the vaccine will be protected from severe rotavirus illness.
Rotavirus Treatment
The best way to protect against dehydration is to drink plenty of liquids. Oral rehydration solutions that you can get over the counter in U.S. food and drug stores are most helpful for mild dehydration. Severe dehydration may require hospitalization for treatment with intravenous (IV) fluids, which are given to patients directly through their veins. If you or someone you are caring for is severely dehydrated, contact your doctor.
Rotavirus Vaccine
An oral vaccine against rotavirus infection, a common cause of diarrhoea and sickness, is given as two doses for babies aged 8 and 12 weeks, alongside their other routine childhood vaccinations.
The vaccine is given as a liquid from a dropper straight into the baby’s mouth for them to swallow.
Source :- Mayo Clinic
CDC
NHS

Leave a Reply