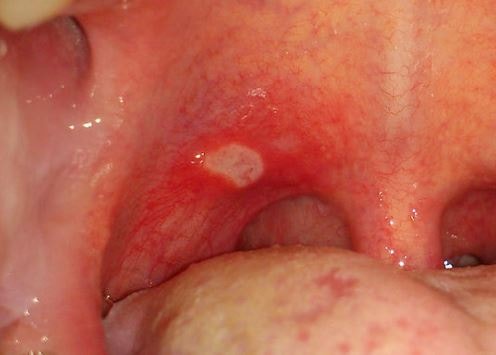
Strep throat is a bacterial infection that causes inflammation and pain in the throat. This common condition is caused by group A Streptococcus bacteria. Strep throat can affect children and adults of all ages. However, it’s especially common in children between the ages of 5 and 15. Sneezing and coughing can spread the infection from one person to another.
Symptoms of strep throat
The severity of strep throat can vary from person-to-person. Some people experience mild symptoms like a sore throat, whereas other people have more severe symptoms including fever and difficulty swallowing. The common symptoms of strep throat include:
- a sudden fever, especially if it’s 101?F or higher
- a sore, red throat with white patches
- a headache
- chills
- a loss of appetite
- swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- trouble swallowing
The symptoms of strep throat typically develop within five days of exposure to the bacteria.
In addition to the common symptoms mentioned earlier, such as sore throat, fever, and difficulty swallowing, a dry throat can also be a symptom of strep throat. When the throat becomes inflamed due to the bacterial infection, it can lead to a dry and scratchy sensation.
Strep throat causes inflammation in the mucous membranes of the throat, resulting in discomfort and dryness. The dryness may be accompanied by a persistent urge to clear the throat or a feeling of roughness. This symptom can vary in intensity from person to person.
It’s important to note that a dry throat alone is not a definitive indicator of strep throat, this is why it is important to identify that most common causes of dry throat. Many other conditions, such as allergies, dehydration, or even excessive talking or breathing through the mouth, can also cause dryness in the throat. Therefore, it’s crucial to consider other accompanying symptoms and consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
When to see your doctor
Not all sore throats are a result of a strep infection. Other illnesses can cause a sore throat, too. This includes:
- the common cold
- a sinus infection
- postnasal drip
- acid reflux
Sore throats caused by other medical conditions usually improve on their own with or without treatment in a few days.
Call your doctor if you experience:
- a sore throat that lasts longer than two days
- a sore throat with white patches
- dark, red splotches or spots on the tonsils or the top of the mouth
- a sore throat with a fine, sandpaper-like pink rash on the skin
- difficulty breathing
- difficulty swallowing
Diagnosing strep throat
If you complain of a persistent sore throat, your doctor will examine your throat and check for signs of inflammation. Your doctor may also check your neck for swollen lymph nodes and ask about other symptoms. If your doctor suspects you have strep throat, they may do a rapid strep test in the office.
This test determines whether your sore throat is caused by a strep infection or another type of bacteria or germ. Your doctor swabs the back of your throat with a long cotton swab, collecting a sample. Your doctor will then send the sample to the lab to look for signs of bacteria.
Results are available in about five minutes. If your rapid strep test is negative but your doctor thinks that you have strep throat, they can send your sample to an outside lab for additional testing. These results are available within a few days.
- Treating strep throat
- Antibiotics
If you’re diagnosed with strep throat, your doctor will prescribe an antibiotic to treat the infection. These medications inhibit the spread of bacteria and infections. Several types of antibiotics are available. However, penicillin and amoxicillin are the most common medications given for a strep infection.
It’s important that you finish your antibiotic treatment course to kill the infection completely. Some people stop taking their medication when symptoms improve, which can trigger a relapse. If this happens, the symptoms can return.
At-home care
In addition to antibiotics, there are at-home treatments to improve the symptoms of strep throat. These remedies include:
- drinking warm liquids, such as lemon water and tea
- drinking cold liquids to help numb the throat
- turning on a cool-mist humidifier
- taking over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen
- sucking on throat lozenges
- adding 1/2 teaspoon of salt to 1 cup of water and gargling the mixture
Outlook and potential complications of strep throat
If strep throat is treated, the symptoms will improve within one week. But if it’s left untreated, strep throat can cause serious complications. These complications include:
- ear infection
- sinusitis
- rheumatic fever, which is an inflammatory disease that affects the joints, the heart, and the skin
poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis, which is an inflammation of the kidneys - mastoiditis, which is an infection of the mastoid bone in the skull
- scarlet fever, which occurs when toxins created by the strep infection cause a scarlet-colored rash to develop on different parts of the body
- guttate psoriasis, which is a condition that causes small, red teardrop-shaped spots to appear on the body
- peritonsillar abscess, which is a pus-filled infection that develops in the back of the tonsils
To reduce your risk of complications, contact your doctor or ent specialist if your strep throat symptoms don’t improve within 48 hours of taking an antibiotic. They may need to prescribe a different antibiotic to fight the infection
Source :-HealthLine

Leave a Reply